Page 61 - IAT
P. 61
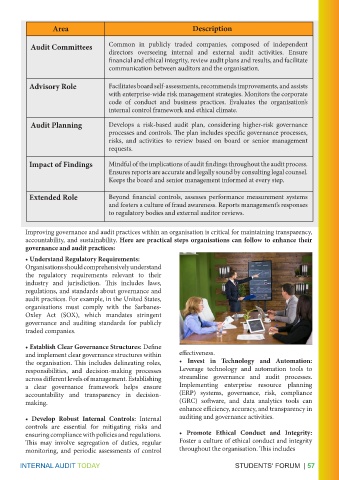
Area Description
Audit Committees Common in publicly traded companies, composed of independent
directors overseeing internal and external audit activities. Ensure
financial and ethical integrity, review audit plans and results, and facilitate
communication between auditors and the organisation.
Advisory Role Facilitates board self-assessments, recommends improvements, and assists
with enterprise-wide risk management strategies. Monitors the corporate
code of conduct and business practices. Evaluates the organisation’s
internal control framework and ethical climate.
Audit Planning Develops a risk-based audit plan, considering higher-risk governance
processes and controls. The plan includes specific governance processes,
risks, and activities to review based on board or senior management
requests.
Impact of Findings Mindful of the implications of audit findings throughout the audit process.
Ensures reports are accurate and legally sound by consulting legal counsel.
Keeps the board and senior management informed at every step.
Extended Role Beyond financial controls, assesses performance measurement systems
and fosters a culture of fraud awareness. Reports management’s responses
to regulatory bodies and external auditor reviews.
Improving governance and audit practices within an organisation is critical for maintaining transparency,
accountability, and sustainability. Here are practical steps organisations can follow to enhance their
governance and audit practices:
• Understand Regulatory Requirements:
Organisations should comprehensively understand
the regulatory requirements relevant to their
industry and jurisdiction. This includes laws,
regulations, and standards about governance and
audit practices. For example, in the United States,
organisations must comply with the Sarbanes-
Oxley Act (SOX), which mandates stringent
governance and auditing standards for publicly
traded companies.
• Establish Clear Governance Structures: Define
and implement clear governance structures within effectiveness.
the organisation. This includes delineating roles, • Invest in Technology and Automation:
responsibilities, and decision-making processes Leverage technology and automation tools to
across different levels of management. Establishing streamline governance and audit processes.
a clear governance framework helps ensure Implementing enterprise resource planning
accountability and transparency in decision- (ERP) systems, governance, risk, compliance
making. (GRC) software, and data analytics tools can
enhance efficiency, accuracy, and transparency in
• Develop Robust Internal Controls: Internal auditing and governance activities.
controls are essential for mitigating risks and
ensuring compliance with policies and regulations. • Promote Ethical Conduct and Integrity:
This may involve segregation of duties, regular Foster a culture of ethical conduct and integrity
monitoring, and periodic assessments of control throughout the organisation. This includes
INTERNAL AUDIT TODAY STUDENTS' FORUM | 57